Layout
Vue NodeGui uses a layout system to automatically arrange child components within a component to ensure that they make good use of the available space.
Fixed Dimensions#
A component's height and width determine its size on the screen. The simplest way to set the dimensions of a component is by adding a fixed width and height to style. Setting dimensions this way is common for components that should always render at exactly the same size, regardless of screen dimensions.
Dynamic Layouts#
Dynamic layouts automatically position and resize components when the amount of space available for them changes, ensuring that they are consistently arranged and that the user interface as a whole remains usable.
Vue NodeGui currently supports creating layouts using FlexLayout.
FlexLayout#
FlexLayout allows the children to expand and shrink dynamically based on available space. Normally you will use flex: 1, which tells a component to fill all available space, shared evenly amongst other components with the same parent. The larger the flex given, the higher the ratio of space a component will take compared to its siblings.
A component can only expand to fill available space if its parent has dimensions greater than 0. If a parent does not have either a fixed width and height or flex, the parent will have dimensions of 0 and the flex children will not be visible.
Flexbox is designed to provide a consistent layout on different screen sizes. You will normally use a combination of flex-direction, align-items,and justify-content to achieve the right layout.
Example#
Lets say you want to build a UI that has a parent view which has two child components. One a label with text Hello and another a view with background color white. Now you want the label to occupy 1/4 of the available height while the white colored child view to occupy the remaining 3/4 height.
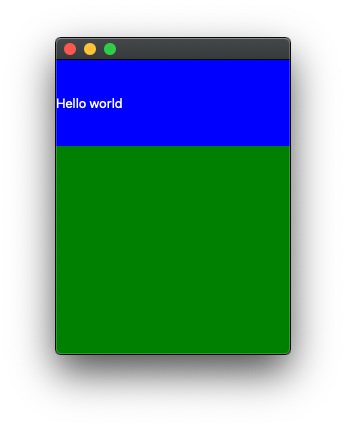
The code for that would look something like below:
To know more on how FlexBox layout works in depth you can visit: https://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/0.60/flexbox. NodeGui uses the same library that React Native uses underneath for FlexBox (Yoga).
You can specify layout properties via inline styles also.
Conclusion#
The primary layout in Vue NodeGui is the Flexbox layout. Flexbox layout can be controlled via stylesheet just as in web. So both paint and layout properties are available at the same place.